Program That Manages Wireless Network For Mac Name
When it comes to helping you troubleshoot wireless networking problems, Mac OS X can't seem to make up its mind. The old Network Utility was appropriate primarily for network gurus. OS X 10.4 came with Network Diagnostics, which took a user-friendlier hand-holding approach. Lion added Wi-Fi Diagnostics, but hid it away; it was largely intended to be used by AppleCare technicians or Apple Store Geniuses, who’d use it to generate detailed log reports. Now Mountain Lion comes with a network tool—a revised version of Wi-Fi Diagnostics—that’s once again intended for regular end users, not just network experts.
- Wireless Network Watcher
- Wireless Networks Journal
- Program That Manages Wireless Network For Mac Name Origin
- Wlan
- Wireless Network Distance
Wireless Network Watcher
Right-click the Wireless Network Connection icon located at the bottom right of your screen, next to the clock and click Open Network and Sharing Center. QUICK TIP: You can also go to Control Panel > Network and Internet > Network and Sharing Center. Network Name: Technically known as the SSID (Service Set Identifier), this is the name that a Wi-Fi base station broadcasts. Multiple base stations may share the same name, to provide roaming. While there’s a lot about Mac OS X that I think is wonderfully crafted, changing the default email program (or Web browser, for that matter) is pretty baffling.
Wi-Fi Diagnostics can help you figure out why your Mac’s Wi-Fi adapter isn’t connecting to a network. It can also find nearby networks (which in turn can be useful for tracking down interference problems) and services broadcasting their availability via Bonjour. It also offers a graphical front end to some common Unix network tools, much as Network Utility did, but in a form that those without command-line experience can use.
To launch Wi-Fi Diagnostics, hold down the Option key as you click on the Wi-Fi icon in the menu bar. That’ll open the Wi-Fi menu with an Open Wi-Fi Diagnostics item at the bottom; click that item to open the utility. You can also launch the program directly from its hidey-hole: In the Finder, choose Go > Go to Folder, and enter /System/Library/CoreServices/. You’ll find the Wi-Fi Diagnostics app in there.
However you open it, you’ll see a welcome window with three options: Create Diagnostic Report, Turn on Debug Logs, and Capture Network Traffic. For your troubleshooting purposes, you can ignore all three and instead choose File > Network Utilities (or press Command-N).
The Network Utilities window provides four separate tabs that are each useful in their own way. Let’s go through them one at a time.
Performance
The Performance view tracks the wireless connection between your Mac and the base station to which it’s connected. The top chart, Signal Strength, shows the relative quality of the connection, while the bottom, Network Traffic, shows bytes passing back and forth. Together, these charts can help you figure out the optimum place to connect to a network or to troubleshoot dead spots in your home or office.

On the Signal Strength chart, the upper yellow line shows the power of the signal being received from the base station while the lower green line shows noise. The further these two lines are from each other, the greater the throughput you will receive. The higher the signal level, the stronger the signal.
Noise often remains constant; if you walk around your home or office with your laptop, that line may not change at all. The yellow signal line is more responsive, and you can watch it change as you move around (or walk between a computer and the direct path to a base station).
The Network Traffic chart below may be less useful than the Signal Strength chart, because it just shows the quantity of data being transferred over your Mac’s wireless connection. But it can tell you whether any data is getting through.
Wi-Fi Scan
The Wi-Fi Scan view shows the results of a scan of the surrounding networks, presenting as much detail about each as it can without actually connecting. The scan can be updated by selecting Active Scan or Passive Scan from the Scan pop-up menu in the lower left; it also updates periodically without intervention. (An active scan may find more networks that broadcast less or no information about themselves.)
Here’s what all the information means:
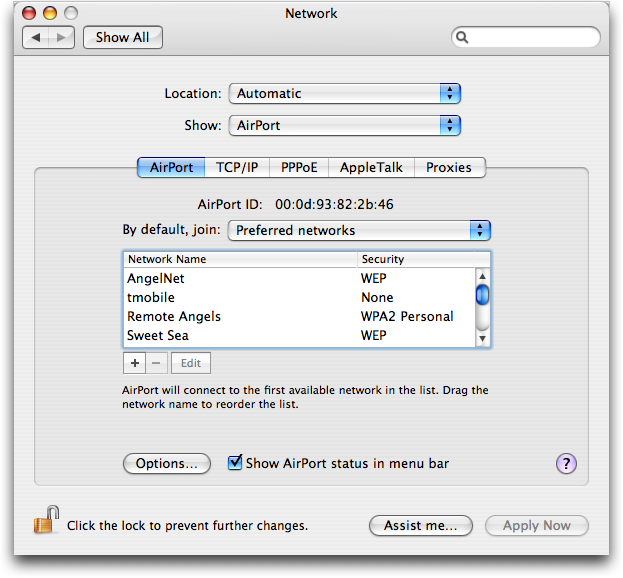
Network Name: Technically known as the SSID (Service Set Identifier), this is the name that a Wi-Fi base station broadcasts. Multiple base stations may share the same name, to provide roaming.
BSSID: The factory-assigned, uniquely numbered address for the base station’s Wi-Fi radio or radios.
Channel and Band: Wi-Fi can operate in two frequency bands: 2.4GHz and 5GHz. Depending on the country, you’ll find channels 1 to 14 in 2.4GHz and 36 to 167 in 5 GHz. (They go up in increments of four, with some gaps.) The Channel and Band columns show which channel a base station offers in which band. Simultaneous dual-band base stations have two listings, one for each band.
Width: It’ll be either 20 MHz or 40 MHz, which refers to the “wide” channel option that doubles throughput but requires two channels to function. Apple only allows its base stations to use wide channels in 5GHz.
Security: The acceptable methods for connecting appear, such as WPA and WEP.
Signal and Noise: Same as the numbers explained above, representing the strength of signal and noise. Again, the bigger the difference, the better the signal.
Protocols: The scan shows the standards being used the various Wi-Fi devices near you. 802.11a and b are the oldest, dating to 1999; 802.11g debuted in 2003; and 802.11n matured in 2007.
CC: The country code for a given device indicates the regulatory domain in which it’s set to operate. If you’re in the US and it doesn’t show US, someone could be violating federal telecommunications law.
Bonjour
The Bonjour tab reveals the services that Bonjour-compatible devices around you are advertising. Each entry shows a particular service, such as iTunes Sharing, and the Bonjour-style address in URL form to reach it. Double-click one of those entries, and OS X will launch the corresponding program and attempt to open that URL.
The Bonjour view provides “negative” knowledge, as well as positive: You can see which devices are talking, but also, by inference, which ones aren’t on the network.
Tools
The Tools tab gives you a graphical interface to a bunch of common networking diagnostic tools; many of them are also found in Network Utility, but in a much less friendly form.
The tools include ping and ping6 for checking whether a remote system is responsive; netstat which provides (exceedingly technical) details about connections in progress by a computer’s network adapter; and whois, which looks up domain registration information.
Wireless Networks Journal
The gear menu changes contextually based on which of command is selected. With ping, for instance, you can pick the number of pings (attempts to test for a machine being alive) as well as the time-gap between them and the size of the packets used in those attempts. With lookup, which pulls down domain name system (DNS) records, you can type in a domain name and select Mail Exchanger (MX) to retrieve which mail servers handle messages for that domain.
While you may not spend a lot of time diagnosing wireless connectivity issues, it’s nice to know that there’s a tool that regular mortals—not just network nabobs—can understand. If nothing else, it’ll make it easier to get help when you can explain to someone else exactly what’s going—or not—on your wireless net.
To request a network license file for your Autodesk software youwill need to find the hostname and physical address of theserver(s) that will be running the Network License Manager(NLM). This information, along with your product serialnumber, is sent to Autodesk and is used to generate a networklicense file that enables you to run the NLM.
About your hostname and physical address
Here are a few notes that will help with identifying the correctinformation and submitting it when you request a network licensefile:
- Ethernet Adapter: If your server has more thanone Ethernet adapter, select one that corresponds to a physicalnetwork adapter. Do not use the physical address for any wirelessor Bluetooth devices, as these are not valid and your networklicense will not work.
If there is more than one physical Ethernet connection on a Windowssystem, it does not matter which one you use. If you are using aMac OS X computer with more than one physical network adapter, youmust use the address of the primary network adapter. - Hostname: The unique identifier that serves as the nameof your computer or server can be as long as 255 characters andconsists of numbers and letters.
- Physical address: Refers to the physical address of theEthernet connection to your computer or server. This may also bereferred to as your MAC (Media Access Control)Address, Host ID or ServerID. It is twelve characters long and is a combination ofnumbers (0–9) and letters (A–F, a–f). Your physical address isoften presented in this format: XX-XX-XX-XX-XX-XX.
- Name and address syntax: When requesting anetwork license file, make sure you have accurately identifiedcharacters that may look similar, such as:
- The number zero (0) and the letter O.
- The number one (1) and uppercase and lowercase 'L' anduppercase 'I' (depending on font).
Program That Manages Wireless Network For Mac Name Origin
Find using the command prompt (Windows only)
To find your hostname and physical address using theWindows Command Prompt:
- Open the Command Prompt window by clicking on Start> (All) Programs > Accessories > CommandPrompt.
Note: If you do not have access to the Command Prompt,please contact your IT department or someone withadministrative rights to your machine to help you locate theinformation. - Type
ipconfig /alland press the Enterkey.
Your hostname will appear at the top, under the sectionWindows IP Configuration:
Your physical address will appear under thesection Ethernet adapter Local Area Connection:
Find Using LMTOOLS (Windows only)
If you already have the Autodesk Network LicenseManager installed on a Windows system, you can use the LMTOOLSUtility to locate your server information.
To find your hostname and physical address using theLMTOOLS utility:
- Open the LMTOOLS utility by clicking Start> All Programs > Autodesk > Network LicenseManager > LMTOOLS Utility.
- Click on the Systems Settings tab.
In the left column titled Hostid Settings you will find yourhostname located in the Computer/Hostname box andyour physical addresslocated in the Ethernet Address box.
Find Using a Terminal Window (Linux or Mac)
If you already have the Autodesk Network LicenseManager installed on a Mac or Linux system, you can use the lmutilutility to locate your server information.
To find your hostname and physical address using a Mac orLinux Terminal Window:
Wlan
- Launch a Terminal window.
- Type in the commands to navigate to the directory wherelmutil is installed. Here's an example:
cd /usr/local/flexnetserver/ - Type the command below to display your Host Name:
./lmutil lmhostid -hostname
You will see a message similar to the one below:lmutil - Copyright (c) 1989-2013 Flexera Software LLC. AllRights Reserved.
The FlexNet host ID of this machine is'HOSTNAME=Nostromo' - Type the command below to display your physicaladdress (Host ID):
./lmutil lmhostid
You will see a message similar to the one below:lmutil - Copyright (c) 1989-2013 Flexera Software LLC. AllRights Reserved.
The FlexNet host ID of this machine is '6003089af239'